Frozen Shoulder VS. Adhesive Capsulitis
July 8th, 2011
 Did you know that frozen shoulder and adhesive capsulitis are actually two separate conditions.
Did you know that frozen shoulder and adhesive capsulitis are actually two separate conditions.
What separates these two diagnoses? Both show up looking like a painful, stiff shoulder. But adhesive capsulitis (as its name implies) affects the fibrous ligaments that surround the shoulder and form what’s called the capsule. The condition referred to as a frozen shoulder usually doesn’t involve the capsule.
The terms frozen shoulder and adhesive capsulitis are often used interchangeably. In other words, the two terms describe the same painful, stiff condition of the shoulder no matter what causes it. A more accurate way to look at this is to refer to true adhesive capsulitis (affecting the joint capsule) as a primary adhesive capsulitis. 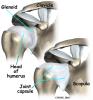
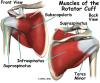
Secondary adhesive capsulitis (or true frozen shoulder) might have some joint capsule changes but the shoulder stiffness is really coming from something outside the joint. Some of the conditions associated with secondary adhesive capsulitis include rotator cuff tears, biceps tendinitis, and arthritis.
How does the orthopedic surgeon diagnose one from the other? An accurate diagnosis is made when an arthroscopic exam is done. Tissue samples taken from inside and around the joint are examined under a microscope.
But there are some clinical signs that help without doing an arthroscopic exam. For example, in the early stages of adhesive capsulitis, pain is accompanied by stiffness and loss of full passive shoulder motion. External rotation is affected first. The rotator cuff remains strong. These two symptoms differ from secondary adhesive capsulitis (what might otherwise be called a frozen shoulder). The condition referred to as a frozen shoulder is more often characterized by damage to the rotator cuff and loss of internal rotation first.
Andrew S. Neviaser, MD, and Jo A. Hannafin, MD, PhD. Adhesive Capsulitis. A Review of Current Treatment. In The American Journal of Sports Medicine. November 2010. Vol. 38. No. 11. Pp. 2346-2356.
Information and pictures sourced from Orthopod
Filed in Patient Information Area
posted by: Bryan Shopka